Why is the boot process of different motherboards different? Why is it that I installed the SSD but the boot process is only slightly faster than the HDD?
This is a question that is asked quite a lot, especially among newbie users, because simply not everyone understands the essence of the problem. So today's article I will talk more deeply why there are different boot stories between systems.

Main Steel Legend's POST code indicator
Firstly, it is related to the POST (Power On Self Test) process of the motherboard. About what POST is, please refer to the information on GOOGLE because there are many articles that clearly explain this issue, so just search for a few related phrases and there are some easy-to-understand articles to help you better understand about POST. its mechanism of action.
To be more specific, during the POST process, the main task of the motherboard BIOS will take care of:
- Check the integrity of CPU registers (Register).
- Check BIOS integrity.
- Check the operation of basic components on the system, for example Direct Memory Access (DMA), I/O...
- Initialize system memory, controller...
- Initialize the chipset.
- Initializes and categorizes devices and system buses and provides a user interface for system configuration.
When the power button is pressed, the system initially checks the stability of the power supply with system control located in the BIOS. Power is on, Mainboard sends Reset > CPU signal via chipset, CPU initializes and waits for Power Good signal. If the voltage is stable, the Reset signal is rejected. The CPU then executes commands that lead to the BIOS boot code, which checks if the hardware devices on the motherboard are working properly. In general, the POST process takes place according to the path. as follows: Power > CPU > ROM > BIOS > Real-time Clock > DMA > 64KB RAM > IRQ > VGA and other I/O devices. When the test is OK, the system will boot successfully and the screen will display the system information.
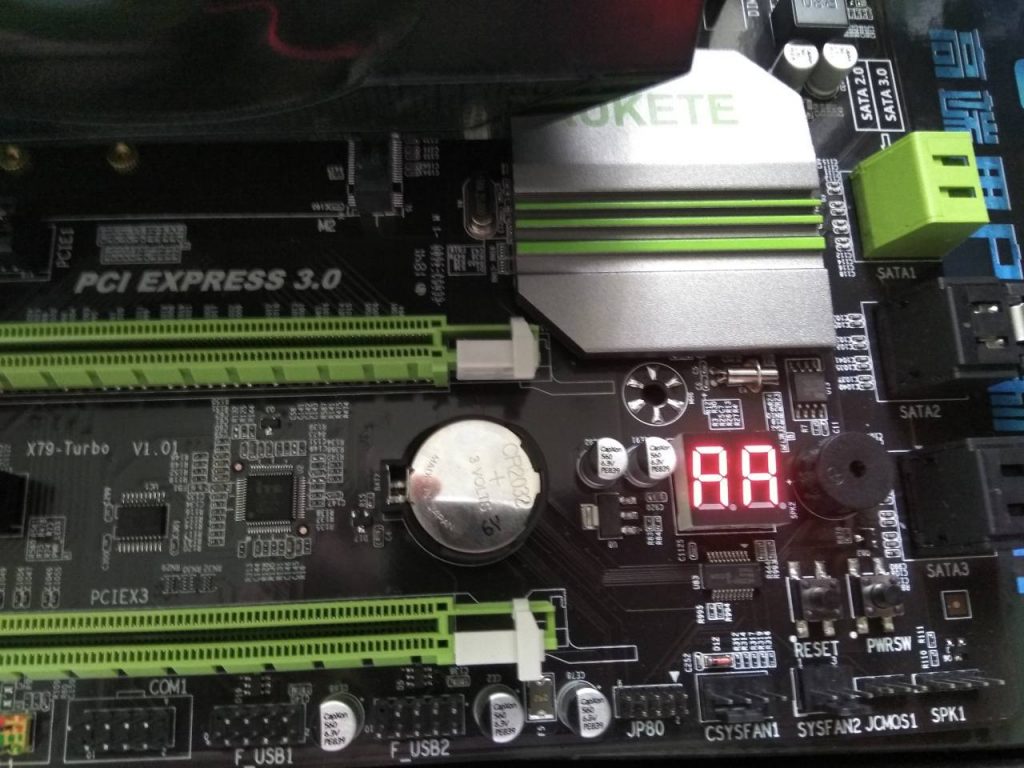

Because this POST process takes place sequentially one by one, each device will have a code to check for errors when POSTing, if there is a problem from a certain component, there will be a corresponding code output. presently. So we will see many motherboards with LED Debug Code available for users to read the code to know where the error is, or have to use the Test Main card with the same method as the embedded LED Debug Code.
Newer, more expensive, and high-end motherboards will take longer to test as there are so many components and components on top of it, obviously, since POST takes longer to process. For example, turning on the RAID function, installing a PCIe SSD on the PCIe slot… also shows that the POST process is slower than usual.
In addition, AMD systems often have slower boot times than Intel systems. This is related to the optimization of the AGESA microcode, with motherboards/processors supporting the AGESA 1.0.0.4 microcode and earlier, the boot time is very long. However, in the new AGESA versions and new platforms, AMD's boot times have been greatly improved.
Most of the booting process is quite fast and smooth, but if it is too slow, try to clear CMOS, Update BIOS and check the components on the system for damage or loose places.

